
- 48 Hour Chick Embryo Cross Section
- 48 Hour Chick Embryo Serial Cross Section Diagram
- 96 Hour Chick Embryo
| Student Outline | Developmental and Physiological Aspects of the Chicken Embryonic Heart |
Introduction
The development of the heart involves a series of cellular migrations, fusions, and specific differentiations, i.e., a multitude of morphogenetic mechanisms.| The heart of the chicken embryo develops from the fusion of paired precardiac mesodermal tubes located on either side of the developing foregut, on the ventral surface. Between 25 and 30 hours of incubation, the paired heart vesicles begin to fuse at the anterior (head) end and continue to fuse posteriorly to form one continuous tube. After fusion is complete, the heart tube is ventral to the foregut and has four distinct regions that can be identified from anterior to posterior: conotruncus, ventricle, atrium, and sinus venosus. Blood flows anteriorly, from the sinus venosus to the conotruncus. At approximately 33 hours the heart tube bends to form an 'S' shape, with the prominent ventricle bulging to the right. | Dorsal view of a 33-hour chicken embryo. The conotruncus (ct), ventricle (v), atrium (a), and sinus venosus (sv) are evident within the S-shaped heart. |
| By 48 hours, the heart has folded upon itself, forming a single loop. This moves the sinus venosus and atrium to a position anterior and dorsal to the ventricle and the conotruncus. The ventricle is U-shaped and in the medial ventral position. Now, the blood flows posteriorly and then makes a sharp turn to flow anteriorly. 56-hour chicken embryo. |
| In the 72-hour embryo, the atrium has begun to expand to the left in preparation of the division into the right and left atria. Although the heart still has two chambers at this time, communication between the sinus venosus and the atrium is via the right side of the atrium. This is the first step towards the sinus venosus becoming part of the future right atrium. The conotruncus will eventually give rise to the aorta. The heart begins to beat just after the paired heart rudiments begin to fuse, immediately before the conotruncus forms. Once the heart tubes have completely fused, the sinus venosus becomes the embryonic pacemaker. Eventually, when the atrium and ventricle each divide into a pair of chambers, and a typical four-chambered heart is present, the sinus venosus is incorporated into the right atrium where it gives rise to the sinoatrial node, the mature pacemaker. | The atrium is now expanded on the right and left sides |
This lab has six goals:
- To identify the anatomy of the developing chicken heart.
- To determine if the heart muscle has an intrinsic ability to contract by surgically removing a beating heart from the living embryo.
- To determine which region of the chicken heart controls the heart beat by isolating the atrium, ventricle, and sinus venosus and then observing which regions continue to beat while in isolation.
- To determine the direction of blood flow through the developing heart.
- To show how in vivo, in vitro, and micromanipulative techniques can be used to study developmental and physiological processes.
- To observe the effects of various concentrations of caffeine and/or gin on an embryonic heart. Your written lab report will be based on this component.
- A 48 Hour Embryo The chick embryo has almost doubled in length from 33 to 48 hours. The embryo has turned its head and bent it toward the yolk, so that the left side of its head rests on the yolk sac (like a pillow). Eventually the rest of the body will twist to the left so that the embryo is lying on its left side atop the yolk.
- 72hr chicken embryo viewed with 2X objective (mid/posterior) 72hr chicken embryo viewed with 2X objective (posterior) 72hr chicken embryo sagittal section viewed with 0.6X objective. 72hr chicken embryo sagittal section viewed with 0.6X objective. 72hr chicken embryo serial cross-section viewed with 1X objective.
- 8 - Embryo of chicken (24 hour) w.m. 9 - Embryo of chicken (24 hour) serial transverse sections. 10 - Embryo of chicken (48 hour) w.m. 11 - Embryo of chicken (48 hour) serial transverse sections. 12 - Embryo of chicken (72 hour) w.m. 13 - Embryo of chicken (72 hour) serial transverse sections. 14 - Embryo of chicken (96 hour) w.m.
24-hour Chick Embryo. Serial Cross sections Photograph 01 of 15: 24 Hour Chick Section 2 of 240 through anterior tip of head fold. In this section, the anterior tip of the head fold can be seen. The portions that are visible at this level are portions of the neural folds.
Materials Per Student Pair
- 72-hour old chicken embryos/eggs, in 37 C humidified incubator (7)
- 110 mm diameter glass dishes, lined with cotton (2)
- Scotch Magic Tape (1)
- 20 G needle attached to a syringe (1)
- Fine scissors (2)
- Fine forceps (2)
- 65 mm Syracuse glass dishes (2)
- Chick saline in 45 C water bath (100 ml)
- Test tube rack in 45 C water bath
- Filter paper 'doughnuts' (8)
- Microknife (Tyler, 1994) and/or iris microdissecting scissors (2)
- Test tubes with caps (6)
- Test tube rack on bench top (1)
- 1.5 ml dropping pipettes (6)
- Embryo spoon (1)
- Gooseneck lamp with 100 W bulb (2)
- Large beaker for eggs/embryos after they have been examined
- Dissecting microscope with lighting from above (2)
- Labeling tape and indelible ink pen (1)
- Atlas
- Stop watch or clock with second hand
- Heart models
- Stock solution of 3% caffeine, made with chick saline
- Stock solution of gin, made with chick saline
Making a Windowed Egg
..... - Modified from Cruz {1993}
- Pick up an egg from the incubator, maintaining its horizontal position as you carry it back to your bench. Place the egg, in that horizontal position, in the glass dish that is lined with cotton.
- Place Scotch Magic tape along the long axis of the egg, so that it covers most of the 'top' of the egg. Place 2 more pieces of tape on the egg, on either side of the center piece.
- Cover the rounded end of the egg with a small piece of Magic tape.
- Puncture the rounded end of the egg that is covered by the tape with a 20 G needle. Insert the needle into the egg so that the needle is pointing down. Be careful of your fingers!
- Withdraw 1-2 ml of albumen. This allows the embryo (if there is one) to move away from the upper surface of the egg, where you will be cutting out the window. Save the syringe and the albumin.
- CAREFULLY, puncture the taped-covered top of the egg with the tip of your scissors. (Again, be careful of your fingers.) The location of the puncture should be about a half an inch off center.
- Proceed to cut out an oval opening, pulling up with your scissors so that you are keeping them as far away from the embryo and vitelline envelope as possible.
- The size of the opening depends on the size of the egg; it should be about the size of a quarter. With forceps, remove the shell cap, exposing the window.
- If you are going to observe the embryo for more than a couple of minutes while it is still in the egg, you will need to prevent dehydration; add several drops of the chick saline to the surface of the embryo. If you are going to immediately explant the embryo, do not add any saline. It will prevent the filter paper doughnut from adhering to the vitelline envelop.
- Determine the in vivo heart rate, the number of beats per minute. Record this information in Table 1. Then draw and label a picture of the in vivo embryo (Appendix A).
Explantation of a Chicken Embryo
..... - Modified from Cruz {1993}
- Explantation means an embryo or tissue is removed from its normal environment, in this case the egg, and placed in another location, in this case a dish of saline. This is a useful method because it is much easier to manipulate or operate on an embryo when it is in a dish, rather than in an egg.
- With the forceps, gently pick off any lumps of albumen on the egg's surface until it appears almost dry.
- The next step requires you to place a filter paper doughnut on the blastoderm so it frames the embryo. The filter paper will stick to the vitelline envelop, holding the embryo in the center. You will then cut the filter paper off the surface of the egg, lifting the embryo with it. When you finally free the filter paper, the embryo should be framed within the filter paper. It's then transferred to the dish of warm saline.
- With forceps, gently position a filter paper doughnut on top of the vitelline envelope, framing the embryo. Gently pat the doughnut in place with the tips of the forceps. Wait a minute to allow the vitelline envelope to adhere to the filter paper.
- While waiting, fill one of the small dishes with about a quarter of an inch of warm chick saline and place the dish on the stage of your dissecting microscope. Angle the gooseneck lamp so that it come as close as possible to the dish; this keeps the saline warm. This is a critical step since the chicken embryo's normal body temperature is close to 37 C. Why do you think temperature is such a critical factor?
- Hold one edge of the doughnut with the tips of the forceps and cut the vitelline envelope along the edge of the doughnut with a pair of scissors. Slowly work your way around the rim of the doughnut, carefully checking to see that the vitelline envelope adheres to it.
- Gradually lift the doughnut with the forceps - the embryo should remain within the center of the doughnut. Quickly transfer the explant to the small dish with the warmed chick saline. You can keep the embryo 'upright' so the right side is facing up. Or you can flip over the explant so the surface that was facing the yolk (the left side) is now facing upwards.
- If the embryo doesn't stay attached to the filter paper, this is the time to use your embryo spoon. Remember to change your saline solution several times since much yolk will be transferred using this process.
- Place the dish on the stage of the dissecting microscope.
- To keep the embryo alive as long as possible, place the illuminated gooseneck lamp close to the dish; this will keep the embryo's body temperature close to 37 C. You should also periodically add fresh, warm chick saline.
- Draw and label a picture of the in vitro embryo (Appendix A). In your diagram indicate the direction of the blood flow through the heart.
- Determine the in vitro heart rate, the number of beats per minute. Record this information Table 1. How does this heart rate compare with the in vivo heart rate?
Electrophysiology of the Embryonic Heart
- The 72-hour old chick explant should be oriented so the right side is facing upwards; this allows you to access the beating heart. Add some fresh, warm chick saline.
- Determine the heart rate, beats per minute, of the in vitro heart. Record this information in Table 1. How does this rate compare to the in vivo heart rate?
- Fill a clean small dish with some warm chick saline, about a quarter of an inch deep.
- Surgically remove the beating heart by cutting it above the conotruncus and below the atrium or sinus venosus.
- Observe the beating of the excised heart and record the following information in your lab notebook and the table at the end of the handout.
- Where does the beating begin and end?
- Determine the heart rate, number of beats per minute and record in Table 1. Is it similar to or different from the heart beat in the explanted, in vitro embryo?
- Draw and label a picture of the explanted heart, labeling each region (Appendix A).
- If your explanted heart stops beating, change the saline and place the dish closer to the gooseneck lamp.
Explanted 72-hour
chicken heart
showing isolated
heart chambers:
sinus venosus (sv),
atrium (a) and
ventricle (v). - Use the microknife or iris microdissecting scissors to isolate each of the two or three regions of the heart. If you can not easily identify the sinus venosus and conotruncus, just cut between the atrium and ventricle.
.....
- Observe each isolated tissue and record the following information in your lab notebook and Table 1.
- Does each have an intrinsic heart beat? If so, are they synchronous?
- What is the heart rate for each region? Do they beat at the same rate as the in vivo or in vitro heart?
- Draw a properly labeled picture of the isolated chambers (Appendix A).
Effects of Caffeine and/or Alcohol on Heart Rate
- Prepare the dilutions of the drug with which you chose to work. Make each dilution in one of the test tubes and use the warm chick saline to create the dilutions. Store your labeled test tubes in the test tube rack that's in the 45 C water bath.
- Design a table similar to the one below wherein you recorded all of your previous data. Remember to include both in vivo and in vitro embryonic heart rates before you expose your embryos to the drugs.
- Explant an embryo into a clean dish of saline. Remember, the temperature of the solution that surrounds the embryo has a significant effect on the heart rate. So, keep the embryo and your solutions at a temperature as close to 37 C as possible.
- Be sure to have a baseline heart rate for each embryo before exposing them to the drug.
- Carry out your experiment!
| Embryo # | In vivo Embryo | In vitro Embryo | Explanted heart | Isolated heart chambers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atrium | Ventricle | ||||
| . | . | . | . | . | . |
| . | . | . | . | . | . |
| . | . | . | . | . | . |
| . | . | . | . | . | . |
| . | . | . | . | . | . |
| . | . | . | . | . | . |
Clean Up
- Put all yolk, albumen, and embryos in the beaker.
- Throw the egg shells and cotton in the trash.
- Put the syringes in the red 'Sharps' receptacles.
- Clean your forceps, scissors and microknife with wet paper towel. Be sure to remove all traces of albumen and yolk. Thoroughly dry them with paper towel.
- Clean your bowls, empty and clean the test tubes, and let them air dry.
- WASH YOUR HANDS WITH SOAP AND WATER!
This page was last modified May 27, 1999. Send questions or comments to jxm57@psu.edu
Copyright© 1999 Dr. Jacqueline McLaughlin and Dr. Elizabeth R. McCain All Rights Reserved
This material may not be reproduced without expressed written permission from the authors.
In this article we will discuss about the development stage of chick embryo, fertilized eggs are procured from recognised poultry farm and incubated in the laboratory.
1. Chick: M. 4 Hours of Incubation:
1. Four hours after incubation of the egg shows differentiation of the blastodisc into area pellucida and area opaca. (Fig. 7).
2. One quadrant of area pelluciada becomes thickened, which marks the future caudal end of embryo.
48 Hour Chick Embryo Cross Section
ADVERTISEMENTS:
3. After 7 to 8 hours, the thickening becomes more elongated and represented start of primitive streak.
2. Chick: W.M. 16 Hours Embryo:
Comments:
1. 16 hours after incubation the primitive streak becomes so distinct that embryos are characterized as being in primitive streak stage. (Fig. 8).

2. In fixed and stained slide, w.m. is composed of central furrow, called as primitive groove lined by thickened primitive ridges.
3. At the cephalic end of the primitive streak, closely-packed cells form thickened area, called as Hensen’s node. Part of area pellucida adjacent to the primitive streak shows increased thickness and forms embryonic elliptical shape.
4. Area pellucida assumes elliptical shape.
5. Elongated primitive streak represents long axis of future embryonic body.
6. Caudal end of the streak is that which lies close to the area opaca.
3. W.M. 18 Hours Chick Embryo:
1. It is a W.M. of 18 hours stage of chick embryo.
2. At this stage the dark peripheral area opaca and central translucent area pellucida are distinctly visible.
3. In the anterior part is present the pro-amnion, which is a small and comparatively more translucent region of area pellucida and is characterised by the absence of mesoderm.
4. In the middle of area pellucida, in the posterior half, runs a primitive streak having a primitive groove through its centre. The primitive groove is being bound by primitive folds.
5. In the anterior half of area pellucida, in the middle, runs a neural groove bound by neural folds.
6. The primitive streak and neural groove is separated by a thickening-the Hensen’s node having a small depression in the centre-the Hensen’s pit.
7. The primitive streak gives rise to an out-growth, the notochord immediately below the primitive groove.
4. W.M. of 21 Hours Chick Embryo:
1. It is a W.M. of 21 hours chick embryo.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. At this stage the dark peripheral area opaca and central translucent and colourless area pellucida are distinctly visible.
3. In the anterior part are present the pro-anmnion, which is a small and comparatively more translucent region of area pellucida and is characterised by the absence of mesoderm.
4. In the middle of area pellucida, in the posterior half, runs a primitive streak having a primitive groove through its centre. The primitive groove is being bound by primitive folds.
5. In the anterior half of area pellucida, in the middle, runs a neural groove bound by neural folds.
6. The primitive streak and neural groove are separated by a thickening, the Hensen’s nod having a small depression in the centre of the Hensen’s pit.
7. The primitive streak gives rise to a small outgrowth, the notochord immediately below the primitive groove and to mesoderm on either side.
8. At this stage embryonic and extra ambryonic regions have also become distinguished in the area pellucida.
9. In the anterior most part the ectoderm has given rise to head fold, which is a pocket-like extension of neural folds.

10. With the ectoderm the underlying endoderm is also transformed into a pocket-like structure the -foregut.
11. The proambion is comparatively reduced in size.
5. W.M. of 24 Hours or 4 Pairs of Somites Stage of Chick Embryo:
1. It is a W.M. of 24 hours 4 pairs of somites stage of chick embryo.
2. At this stage the dark peripheral area opaca and central translucent and colourless area pellucida are distinctly visible.
3. In the anterior part is present the proamnion, which is a small and comparatively more translucent region of area pellucida and is characterised by the absence of mesoderm.
4. In the middle of area pellucida, in its posterior half runs a primitive streak with a primitive groove in its centre. The primitive groove is bound by primitive folds.
5. In the anterior half of area pellucida, in the middle, runs the neural groove bound by neural folds.
6. The primitive streak and neural groove are separated by Hensen’s node having a small depression in the centre-the Hensen’s pit.
7. Immediately below the primitive groove the primitive streak gives rise to a small out- growth, the notochord and on either side to mesoderm.
8. In the area pellucida embryonic and extra embryonic regions also become distinguished.
9. In the anterior- most part the ectoderm has given rise to head fold, which is a pocket-like extension of neural folds. The underlying endoderm is also transformed into a pocket-like foregut. The proamnion is greatly reduced.
10. In front of Hensen’s node the mesoderm of embryonic area differentiated into 3-4 pairs of mesodermal somites.
11. The neural canal, in the region of head fold, gives rise to forebrain.
12. The foregut extends on either side into an amino-cardiac vesicle.
6. W.M. of 30 Hours of 8-10 Pairs of Somites Chick Embryo:
1. It is W.M. of 30 hours of chick embryo or 8-10 pairs of somite stage of chick embryo.
2. At this stage the dark peripheral area opaca and central translucent and clourless area pellucida are distinctly visible.
3. In the anterior part is present the proamnion, which is a small and comparatively more translucent region of area pellucida and is characterised by the absence of mesoderm.
4. In the middle of area pellucida, in the posterior half, runs a primitive streak with a primitive groove running through its centre. The primitive groove is bound by primitive folds.
5. In the anterior half of area pellucida, in the middle, runs the neural groove bound by neural folds.
6. The primitive streak and neural groove are separated by Hensen’s node having a small Hensen’s pit in the centre.
7. Immediately below primitive groove the primitive streak gives rise to the notochord and on either side to mesoderm.
8. At this stage embryonic and extra embryonic regions have also become distinguished in the area pellucida.
9. In the anterior-most part, the ectoderm has given rise to head fold which is a pocket like extention of neural folds. The underlying endoderm has transformed into pocket like foregut. The proamnion is reduced.
10. The mesoderm, in front of Hensen’s node, has given rise to 8-10 pairs of somites.
11. In the region of head fold the anterior part of neural canal has given rise to a distinct fore brain.
12. The foregut and cardiac vesicles are sufficiently developed.
13. The extra embryonic area has grown in size.
7. W. M. of 33 Hour Chick Embryo of 11-12 Pairs Somites:
1. It is W.M. of 33 hours chick embryo.
2. At this stage the dark peripheral area opaca and central translucent area pellucida are not distinctly visible.
3. The primitive streak has been comparatively reduced because of great lengthening of neural canal and neural folds.
4. The extra embryonic area has grown in size.
5. The mesoderm, in front of Hensen’s node, has given rise to 11-12 pairs of somites.
6. The foregut and cardiac vesicles are sufficiently developed.
7. The brain is differentiated into fore brain, mid- brain and hind brain.
8. The area opaca has changed into area vasculosa.
9. Proamnion has disappeared.
10. Anterior omphalomesenteric vein has developed.
8. W.M. of Chick Embryo of 13-14 Pairs Somites or 36 Hours:
1. It is W.M. of 36 hours chick embryo.
2. At this stage the dark peripheral area opaca and central translucent and colourless area pellucida are not visible.
3. The extra embryonic area has grown in size.
4. The primitive streak is comparatively reduced because of great lengthening of neural canal and neural folds. The notochord has extended from behind the brain up to the end of body.
5. The mesoderm, in front of Hensen’s node, has given rise to 13-14 pairs of somites.
6. The brain is differentiated into fore brain, mid brain and hind brain.
7. In the fore brain region optic vesicles and in the hind brain region optic vesicles have developed.
8. The area opaca has changed into area vasculosa.
9. Proamnion has disappeared.
10. Anterior omphalomesentric vein and vitelline artery have developed.
11. The cardiac vesicle has given rise to heart.
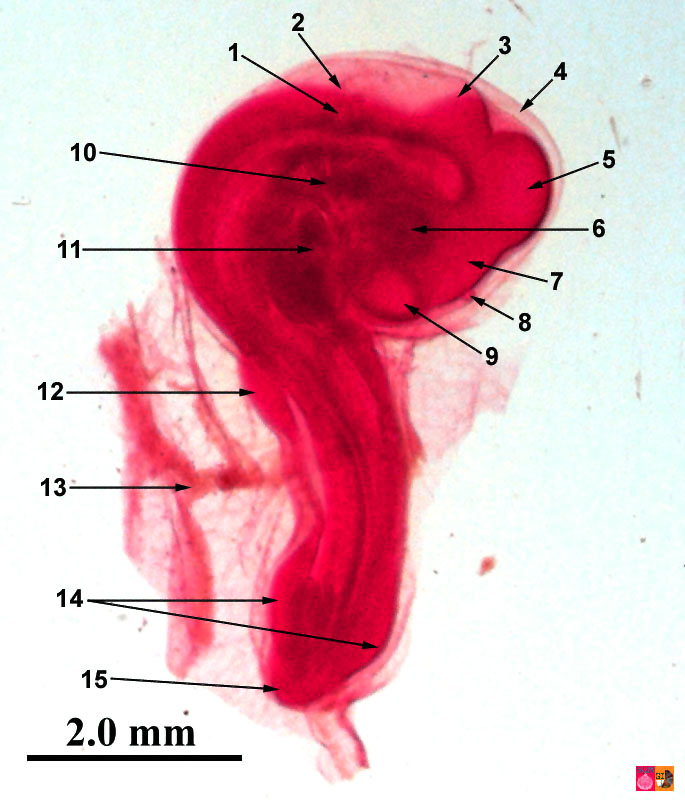
9. W.M. of 48 Hours Chick Embryo of 26-28 Pairs of Somites:
1. It is W.M. of 48 hours chick embryo.
2. At this stage the area opaca and area pellucida are not visible.
3. The extra embryonic area has grown in size.
4. Primitive streak has disappeared.
5. The mesoderm, in front of Hensen’s node, has given rise to 26-28 pairs of somites.
6. The brain has differentiated into telencephalon, prosencephalon, mesencephalon, metancephalon and mylencephalon.
7. The heart has been differentiated into ventricle and atrium. Sinus venosus and truncusarteriosus have also started developing.
8. The eye has been differentiated into optic cup and lens and optic vesicle has also developed sufficiently.
9. The head region has curved on right side due to cranial flexion.
10. Three pharyngeal gill-slits have also been differentiated.
11. Behind Hensen’ node a tail bud has also developed.
12. Lateral amniotic folds, anterior omphalomesentric vein and vitelline artery have appeared.
10. W.M. of 72 Hours or 36 Pairs of Somites Stage of Chick Embryo:
1. It is W.M. of 72 hours chick embryo.
2. At this stage area opaca and area pellucida are not visible.
3. The extra embryonic area has grown in size.
4. Primitive streak has disappeared.
5. The mesoderm, in front of Hensen’s node, has given rise to 36 pairs of somites.
6. The brain has differentiated into telencephalon, mesencephalon, metancephalon and mylencephalon.
7. The heart has been differentiated into ventricle and atrium.
8. The eye has differentiated into optic cup and lens and optic vesicle has also developed sufficiently.
9. The head region has bent on right side due to cranial flexion.
10. Four pairs of gill-slits have been differentiated.
11. Tail bud is greatly developed and has given rise to allentoic stalk and tail.
12. Lateral amniotic folds, vitelline artery and anterior omphalomesentric vein have developed.
13. In the middle region a pair of fore limb buds and in front of tail a pair of hind limb buds have developed, which will give rise to fore and hind limbs.
14. Olfactory pit, visceral arches, amnion, allantois and amniotic cavity have also developed.
48 Hour Chick Embryo Serial Cross Section Diagram
11. W.M. of 96 Hours Chick Embryo:
1. In the chick embryo of 96-hours of incubation, the entire body has been turned through 90 degree and the embryo lies with its left side on the yolk.
2. At the end of 96 hours the body folds have undercut the embryo so that it remains attached to the yolk only by a slender stalk.
3. The yolk salk soon become enclogated, allowing the embryo to become first straight in the mid-dorsal region and then convex dorsally.
4. The progressive increase in the cranial, cervical, dorsal and caudal flexures results in the bending of the embryo on itself so that its originally straight long axis becomes C-shaped and its head and tail lie close together.
5. Optic cup shows the more developed lens.
6. Endo-lymphatic duct arises from the auditory vesicle.
7. Visceral arches have become very much thickened.
8. Appendage buds increase rapidly in size and become elongated.
9. The number of somites increases to 41 pairs.
10. Allantois has also appeared.
11. Omphalomesenteric artery and omphalomesenteric vein are also developed.



